All 12 useState & useEffect Mistakes Junior React Developers Still Make in 2025
📋 Video Summary
🎯 Overview
This video, by ByteGrad, covers the top 12 mistakes junior React developers make with `useState` and `useEffect` hooks. The video aims to help developers avoid common pitfalls and write more efficient and maintainable React code. The video explores each mistake with code examples and solutions.
📌 Main Topic
Common mistakes made by junior React developers when using `useState` and `useEffect` hooks in React.
🔑 Key Points
- 1. Incorrectly Updating State with Multiple Updates [0:00]
- 2. Conditional Rendering and Hooks [0:11]
- 3. Incorrectly Updating an Object's State [0:47]
- 4. Inefficient State Management in Forms [0:59]
- 5. Overuse of `useEffect` for Derived State [1:10]
- 6. Primitives vs. Non-Primitives and Re-renders [1:25]
- 7. Incorrect State Initialization [1:33]
- 8. Type Script Mistakes [1:39]
- 9. Not Using Custom Hooks [1:50]
- 10.Server vs. Client Components and Hooks [2:00]
- 11.Closure Issues with `useEffect` and Intervals [2:09]
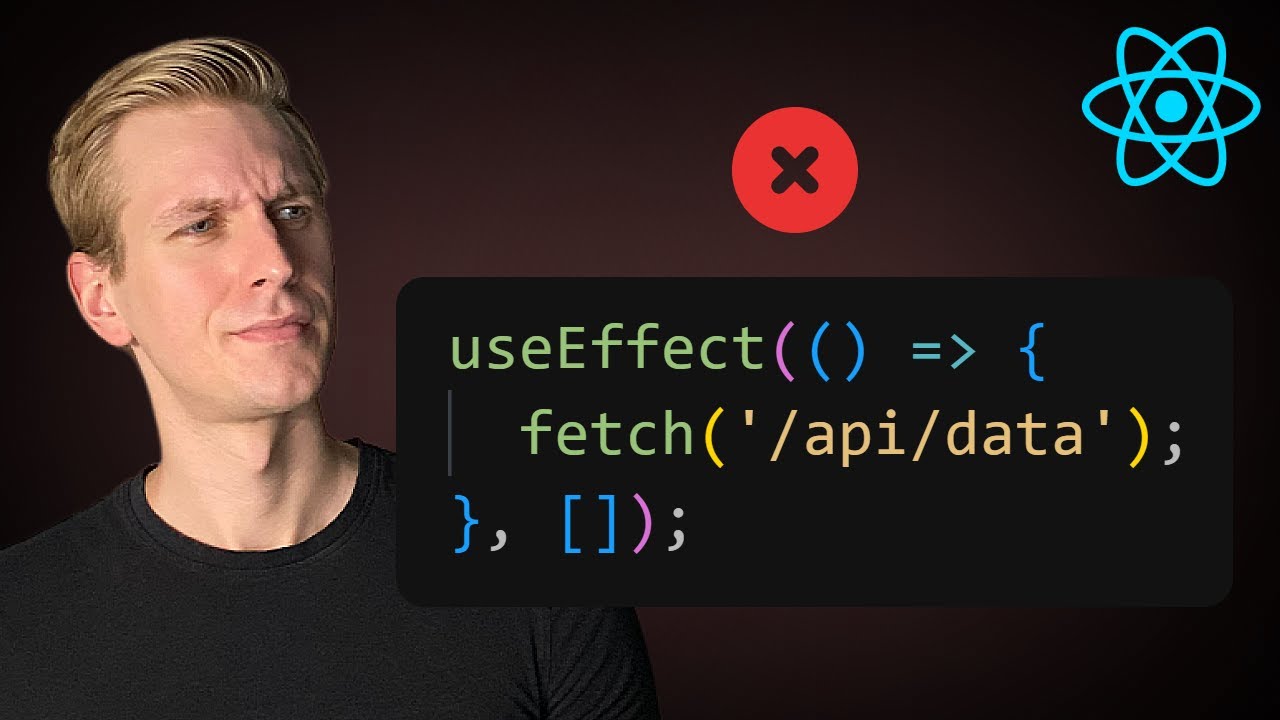
- 12.Fetching Data in `useEffect` Pitfalls [2:19]
💡 Important Insights
- • Dependencies in `useEffect`: When using `useEffect`, be mindful of the dependency array. Include only the variables that, when changed, should trigger the effect. [1:00]
- • Client vs Server Component: Server components run on the server, while client components run in the browser. Using hooks in server components results in errors. [2:00]
📖 Notable Examples & Stories
- • Counter Example: A simple counter example demonstrates the issue of multiple `setState` calls not updating as expected. [0:00]
- • Form Example: A form example illustrates the use of a single state object with dynamic property updates using the `name` attribute. [0:59]
- • Window Size Example: A code example using a custom hook for window size to avoid repetitive code. [1:50]
- • Post Fetching Example: The video shows the problems of race conditions and the need for cleanup in fetching examples. [2:19]
🎓 Key Takeaways
- 1. Understand the nuances of `useState` and `useEffect` to avoid common errors.
- 2. Use best practices for state management, including the updater function for `setState`, single state objects for forms, and custom hooks for reusability.
- 3. Be aware of the differences between server and client components and how they affect the use of hooks.
- 4. Master JavaScript fundamentals to better understand how hooks work.
- 5. Consider professional solutions, such as react query or SWR, when fetching data.
✅ Action Items (if applicable)
□ Review the code examples provided in the video. □ Practice using the techniques discussed in your own React projects. □ Experiment with custom hooks to refactor and reuse logic. □ Consider using libraries like React Query or SWR for data fetching.
🔍 Conclusion
The video provides a comprehensive overview of the most common mistakes junior React developers make with `useState` and `useEffect`. By understanding these mistakes and the solutions, developers can write cleaner, more efficient, and maintainable React code, ultimately leading to better applications.
Create Your Own Summaries
Summarize any YouTube video with AI. Chat with videos, translate to 100+ languages, and more.
Try Free Now3 free summaries daily. No credit card required.
Summary Stats
What You Can Do
-
Chat with Video
Ask questions about content
-
Translate
Convert to 100+ languages
-
Export to Notion
Save to your workspace
-
12 Templates
Study guides, notes, blog posts